The OSI model, an ISO standard since 1984, structures network communication into seven layers, each with specific tasks, facilitating system communication and technological development.
The ISO/OSI reference model is a description standard for network protocols. Development of the model started in 1977. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) was heavily involved in the development. It was published as an ISO standard in 1984.
The OSI model structures the complex world of network communication into seven clear layers. Every layer has its own, precisely defined tasks. The model facilitates communication between different technical systems and promotes the development of new technologies. It makes network protocols interchangeable within the same layer. In short, the OSI model is the backbone for a structured and efficient network design.
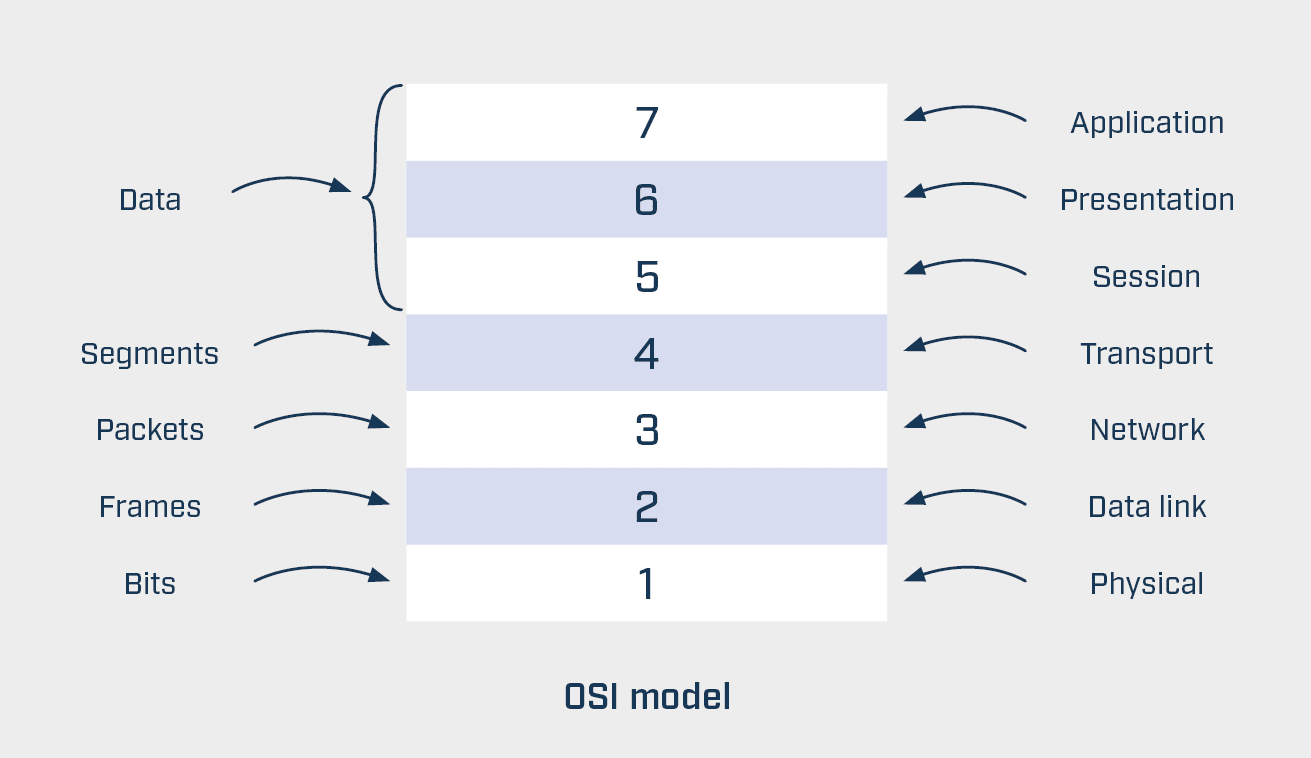
The OSI model structures the networkcommunication into seven clearly defined layers:
- Physical Layer: This is about the transmission of raw data bits via physical connections. This layer deals with hardware components, such as cables, connectors, and physical signals.
- Data Link Layer: This layer guarantees a reliable data transmission by organizing data in frames and performing error detection and correction.
- Network Layer: Responsible for routing data packets across the network. Routers are a typical example of hardware on this level.
- Transport Layer: The data flow is segmented here and the data transmission is monitored to ensure a reliable data delivery.
- Session Layer: Allows the management and control of sessions between two systems by defining restart points, for example.
- Presentation Layer: Responsible for converting the data into a format that is understandable for both communication partners, including encryption and compression.
- Application Layer: This layer offers network services for end applications, making it the interface to the user.
The OSI model is more than just a technical guideline. It is a basic framework that structures and simplifies communication in a digital world. It uses a concept of layers to offer flexibility and clarity in network communication. Even though this is a theoretical model, it has practical effects on the development and understanding of network technologies.

